Coal Enrichment
Coal is a solid hydrocarbon compound that is found in natures with a complex composition. The main organic contents are plants that can be landmarked with bark trails, leaves, roots, wood structure, spores, pollens, resin etc. Afterward those organic materials go through decomposition causing changes in its physical characteristics and also chemically before and after covered by other sediments. Basically there are two types of material that form coals, which are:
Combustible Material, are materials that are combustible or can be oxidized. These materials generally consists of Fixed Carbon, Hydrocarbon compounds, Total Sulfur, Hydrogen Compound and other compounds in small numbers. In the coal forming process, with help from physic and natural chemistry, cellulose (C49H7O44) which comes from plants will go through changes to become Lignite (C70H5O25), Sub-bituminous (C75H5O20), Bituminous (C80H5O15) or Anthracite (C94H3O3).
Non Combustible Material, are materials that are not combustible or cannot be oxidized. These materials are generally shaped by inorganic compounds (Si02, Al203, Fe203, Ti02, Mn304, CaO, MgO, Na20, K20 and other metal compounds in small numbers) which will form the ashes inside the coal.
REDS Energy offers technology of the coal enrichment using pyrolysis process. Pyrolysis is a thermochemical decomposition of organic material at elevated temperatures in the absence of oxygen. It involves the simultaneous change of chemical composition and physical phase. When coal is heating under air-free conditions, the organic matter undergoes a series of changes as the temperature increases, forming gaseous, liquid and solid (semi-coke) products.
Coal pyrolysis can be roughly divided by phases as shown at the table.
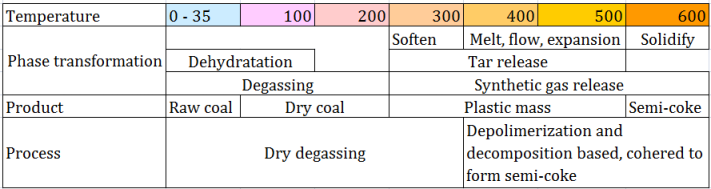
At the first phase of pyrolysis dehydration occurs (below to 120 OC). Raw coal can contain up to 40 % of humidity, water existence in the coal effects negatively to its physical properties, it reduces calorific value and increases the weight ballasted. Also humidity takes on the role of heat ballast during coal combustion in industrial boilers. So dehydration is one of the most important stage of the coal enrichment.
At the same phase (below to 200 OC) removal of gases, such as N2, CH4 and CO2, completes. Lignite decarboxylates and pyrolyzes at about 300 OC. Anthracite and bitumite remains generally unchanged.
The second phase occurs at around 600 OC. Large amount of volatiles (gas and tar) are generated and discharged. The maximum amount of tar is discharged at about 450 OC, and the maximum amount of gas is released at 450-600 OC.
The highly combustible synthesis gas is supplied back to pyrolysis chamber and used like a part of fuel for processing. A tar (pyrolysis liquid), that received through the process of condensation, supposed to be refined with distillation or rectification in trade fuel (diesel EURO IV). Remaining product in pyrolysis chamber is a semi-coke – type of enriched coal with high calorific value, low weight and low content of harmful substances.
The general benefits of coal enrichment by pyrolysis are following:
Increasing of calorific value up to 30 %. End product is a semi-coke with less than 5% humidity and more than 6000 kcal/kg heating value.
Reduction of bulk density and transportation weight as a result.
Removal of the substances, which are contained in light hydrocarbon fraction and form harmful chemical compounds during ordinary combustion.
Receiving of liquid fuel (diesel) like a by-product, that is available for selling to oil traders and wholesalers.
The equipment can be installed in an open pit or in the coal storage. Modular systems can process from 5500 to 110 000 tons of raw coal per year (365 days), with a daily capacity from 15 to 300 tons per day.
Contact Info
Email:
contact@redsenergy.com
Address:
Bulgaria, Sofia, 1142 Sofia Center, Sredets distr., st. Lyuben Karavelov No 26, fl. 1
+63 999-660-3762
LinkedIn:
www.linkedin.com/company/reds-energy-ltd